Activities
Biomedical applications of plant secondary metabolites
- Selection of the bioactive, natural plant products for antioxidant, antiproliferative (using human neuroblastoma and other cell cultures) and/or antimicrobial activities (using human, animal and plant pathogens);
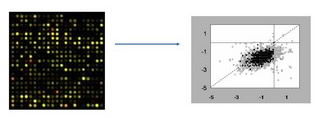
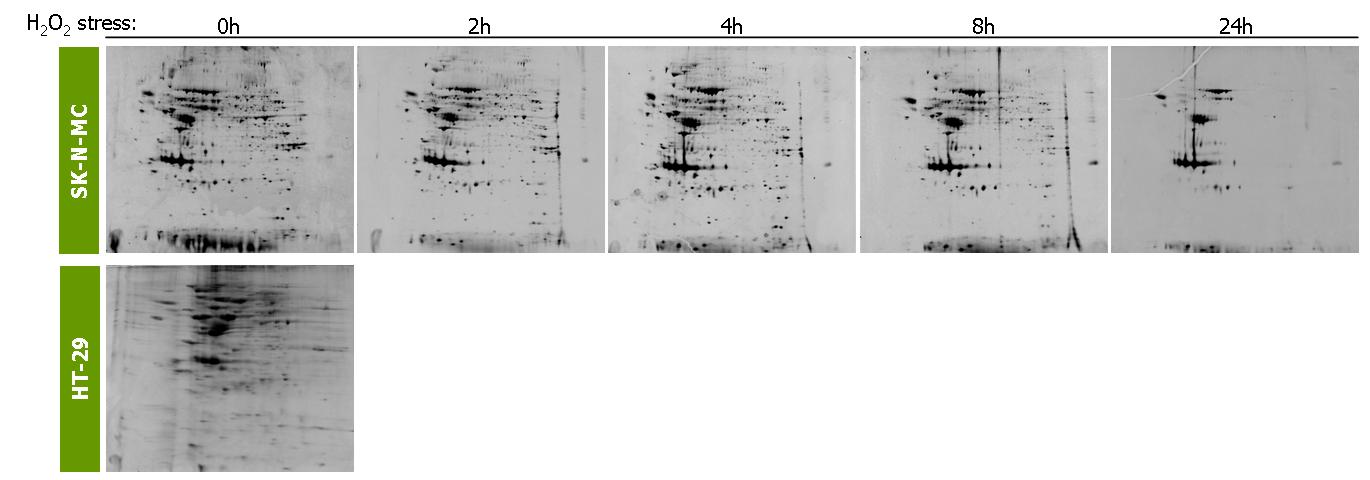
- Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of the bioactive, natural plant products in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, using human neuroblastoma cells (SK-N-MC);
- Proteomic analyses of the bioactive, natural plant products on the prevention of colon diseases;
Transcriptomic analyses
Proteomic analyses
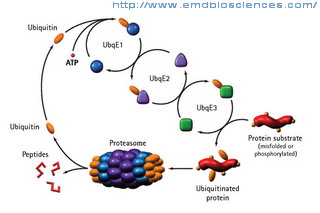
- Effect of treating rotenone-incubated human neuroblastoma cells with bioactive, natural plant products on the role played by the ubiquitin/proteasome system (UPS) in Parkinson´s disease;
- Polyphenols as protective agents in cellular models of alpha-synucleinopaties, in particular Parkinson’s disease:
Effect in yeast strains sensitive to oxidative stress
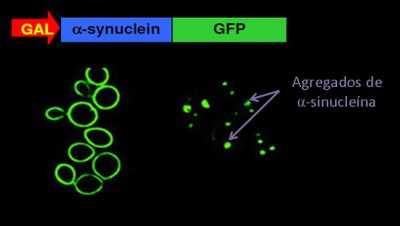
Evaluation of the protective role on the toxicity caused by alpha-synuclein in a PD cellular model induced by its overexpression in a strain of yeast
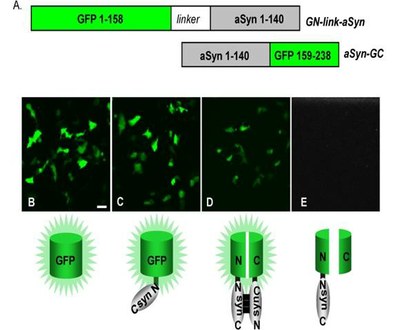
Effect on alpha-synuclein oligomerization by a bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay in the human neuroglioma cell line H4
- Bioavailability of antioxidant compounds after in vitro digestion and human intervention studies of highly antioxidant fruits and other plant organs.
Biodiversity, conservation and bioactivities
- In vitro vegetative propagation of Portuguese endemic species, some of which are under threat of extinction;
- Characterization of novel, bioactive, natural plant products (including polyphenols) of this species.
New and non-toxic strategies to control and fight pathogenic fungi
- Transcriptomic, proteomic & metabolomic analyses of the interaction grapevine/pathogenic fungi; major fungi under study: Uncinula necator (responsible for grapevine powdery mildew) and several fungi responsible for grapevine wood diseases (ex: Phomopsis viticola and Phaeomoniella chlamydospora);
- Action mechanisms of blad antifungal polypeptide;
- Host-induced changes in human fungal pathogen exoglycomes (e.g. Aspergillus fumigatus);
- Transcriptomic & metabolomic changes in Aspergillus fumigatus when challenged by other fungi;
- Transcriptomic, proteomic & metabolomic analyses of the interaction human cells/pathogenic fungi;
- Search & development of novel and non-toxic fungicides, active against human, animal and plant pathogens;
- Stereochemical studies on dirigent protein function;
- Differential approaches to genetically transform grapevine, rose and other plants, by constitutive expression of antifungal (or other) proteins;
- Role of sap long-distance macromolecular trafficking in plant signalling;
- Development of specific bioelectronic methodologies capable of detecting and treating grapevine plants infected with esca and other recalcitrant wood disease-causing fungi.



